Abstract
The autonomic nervous system is an important modulator of electrical disorders observed in cardiac pathologies through changes in the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic tone. The final common pathway for cardiac neuronal autonomic control resides in the intrinsic cardiac nervous system (ICNS), composed of intracardiac neurons (ICN), and which allows sympathetic-parasympathetic efferent neuronal interactions at intracardiac sites. The ICNS is a complex system that plays a crucial role in the regulation of cardiac physiological parameters and has been shown to contribute to cardiac diseases, in particular cardiac arrhythmias. It is therefore crucial to understand the molecular determinants, such as ion channels, that control the excitability of the ICNS and their potential modulation in pathological conditions.
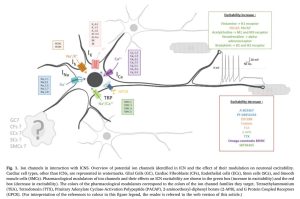
This review discusses several ion channels expressed by ICN, including potassium channels (e.g., inward rectifier, calcium-dependent, voltage-activated, muscarinic-sensitive), voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSC), voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC), hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide – gated (HCN) channels and Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Channels, and their potential involvement in cardiac pathologies. We highlight the need for further research on ICN ion channels, particularly under pathological conditions, to develop therapies for cardiac arrhythmias.
This review discusses several ion channels expressed by ICN, including potassium channels (e.g., inward rectifier, calcium-dependent, voltage-activated, muscarinic-sensitive), voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSC), voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC), hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide – gated (HCN) channels and Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Channels, and their potential involvement in cardiac pathologies. We highlight the need for further research on ICN ion channels, particularly under pathological conditions, to develop therapies for cardiac arrhythmias.
Téléchargez ici le pdf
Informations complémentaires
CANAUX IONIQUES ET NEURONES CARDIAQUES